Tagger Group¶
Tagger Group is for training multiple classes at once and it also uses tags in the dataset given.
Note
- How do Tagger and Tagger Groups differ?
One model predicts whether a text is positive (True) or negative (False). That is, whether this text gets the label or not. Tagger trains only one model and predicts whether a text is similar to the dataset it was trained on or not. Tagger Group trains several models at once. That means, it can predict several labels at once. Tagger Group trains on facts. You can have several values under a certain fact and for each value (if it has high enough frequency (Minimum sample size) a model is trained.
Creation¶
Parameters¶
- description:
Name of the Tagger model, which is also used as name of the tag while tagging the documents.
- indices:
Names of the indices the model learns from (defaults to every index in the Project).
- fields:
The fields the model learns from. If more than one fields is chosen, the fields are concatenated together before the learning process. One field is also enough. Usually lemmatized texts are preferred, especially with morphologically complex languages, because it increases the frequency of some words (eaten, eats and ate will change to its lemma eat and are dealt as one word).
- query:
Searcher’s query for the dataset to be trained on. If Query is left empty, it will take all data in the active project as an input. You can also use saved searches as your desired input. This input will be the positive examples - later on, the Tagger tags data similar to this one.
- embedding:
Embedding previously trained on the same dataset.
- vectorizer:
Hashing Vectorizer, Count Vectorizer, Tfldf Vectorizer - read more about them here.
- classifier:
- maximum sample size:
The maximum sample size per class is for limiting the size of data the model trains on.
- negative multiplier:
The negative multiplier is for changing the ratio of negative examples.
GUI¶
Create a new Tagger Group model by clicking on the ‘CREATE’ button in the top-left. Then choose the parameters. After that, all that’s left is hitting the “Create”-button (scroll down a bit), seeing the training process and the result of the tagger.
Note
LinearSVC might give an error in case there’s not enough data in the search.
Fig. 70 Creating a Tagger Group¶
- Whenever we create new Tagger Group models, we can track its progress from the table under Task. If we click on the job, we can see all the training info, how long did it took, and check how successful it was. Let’s not forget that:
Recall is the ratio of correctly labeled positives among all true positives. Avg.recall is the average of all the models’ recalls.
Precision is the ratio of correctly labeled positives among all instances that got a positive label. Avg.precision is the average of all the models’ precisions.
F1 score is the harmonic mean of these two and should be more informative especially with unbalanced data. Avg.F1_score is the average of all the models’ F1 scores.
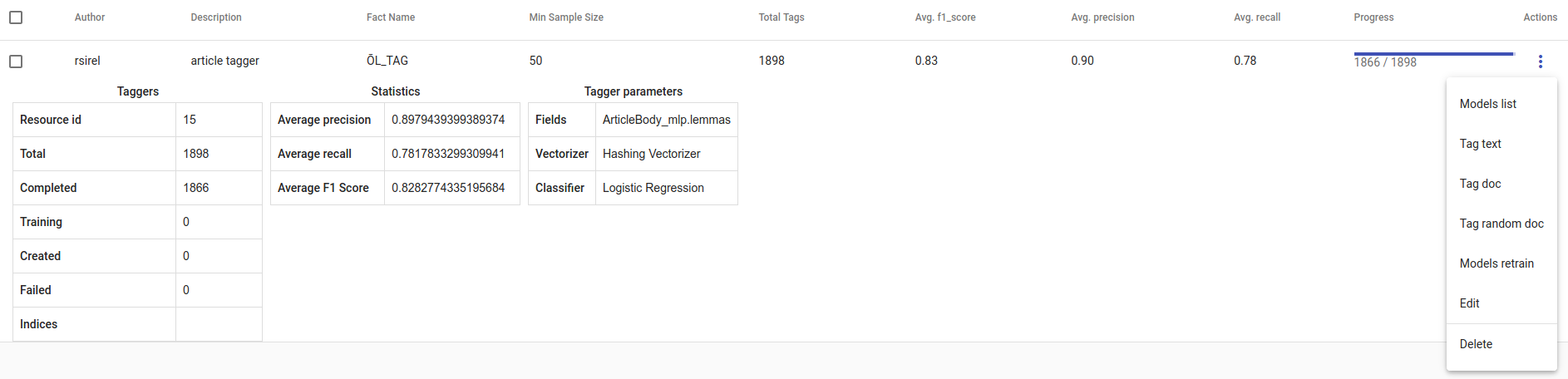
Fig. 71 Created Tagger Group¶
In the table view, you can also select several Tagger Groups and delete them all at once by clicking on the dustbin button next to the CREATE button in the top-left. If you have several Tagger Groups, you can search for the right one by their description or task status. If you have models on several pages you can change pages in the top-right.
API¶
Endpoint: /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/
Example:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/api/v1/projects/11/tagger_groups/" \
-H "accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Token 8229898dccf960714a9fa22662b214005aa2b049" \
-d '{
"description": "My tagger group",
"fact_name": "TEEMA",
"minimum_sample_size": 50,
"tagger": {
"fields": ["lemmas"],
"vectorizer": "Hashing Vectorizer",
"classifier": "Logistic Regression"
}
}'
Trained Tagger Group endpoint: /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/{id}/
Usage¶
Models list¶
Models list displays the models the Tagger Group trained. You can inspect which kind of labels were trained.
API endpoint: /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/{id}/models_list/
Tag text¶
Tag text is to check how does the model work. If you click on that, a window opens. You can paste there some text, choose to lemmatize it (necessary if our model was trained on a lemmatized text), and choose to use NER and post it. You then receive the result (all the labels which model predicted True for this text) and the probability of this label is true. Probability shows how confident is this model in its prediction. Number of similar documents is the number of most similar documents to the document in question. Tags given to these documents are tested on the document to be tagged.
API endpoint: /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/{id}/tag_text/
Example:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/api/v1/projects/11/tagger_groups/1/tag_text/" \
-H "accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Token 8229898dccf960714a9fa22662b214005aa2b049" \
-d '{
"text": "AINUS ettepanek - alla põhihariduse isikutele sõidulubasid mitte anda - sai kriitika osaliseks.",
"lemmatize": true,
"use_ner": false,
"n_similar_docs": 10,
"n_candidate_tags": 10,
"feedback_enabled": false
}'
Response:
[
{
"tag": "foo",
"probability": 0.6659222999240199,
"tagger_id": 4,
"result": true
},
{
"tag": "bar",
"probability": 0.5107991699285356,
"tagger_id": 3,
"result": true
}
]
Tag doc¶
Tag doc is similar to Tag text, except the input is in the JSON format. Number of similar documents is the number of most similar documents to the document in question. Tags given to these documents are tested on the document to be tagged.
API endpoint /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/{id}/tag_doc/
Tag random doc¶
Tag random doc takes a random instance from your dataset, displays it, and returns the positive results of your models and the probability of these results being correct.
API endpoint /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/{id}/tag_random_doc/
Apply to index¶
Used to classify every document inside one or several indices with a Tagger Group, this process will scroll through all the documents, parse the texts of the given fields and return their results as Texta Facts.
Since this is a long-term tasks, the user will get a response immediately while another processes it.
API endpoint /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/{id}/apply_to_index/
Edit¶
Edit is for changing the description.
Models retrain¶
Models retrain retrains all of the Tagger Group models with all the chosen parameters. It’s useful in case your dataset changes or you have added some stop words.
API endpoint /projects/{project_pk}/tagger_groups/{id}/models_retrain/
Delete¶
Delete is for deleting the model.
