ES Analyzer¶
ES Analyzer is a tool for applying various Elasticsearch analyzers to indices. Currently supported analyzers are:
Stemmer
Tokenizer
Creation¶
Parameters¶
- description:
Name of the ES Analyzer application task. This is necessary only for differentiating between all the ES Analyzer tasks in the project.
- indices:
List of Elasticsearch indices containing the documents to analyze. NB! Indices should be formatted as list of dicts, where key = “name” and value = <index_name>, e.g:
[{"name": "my_dataset"}]
- fields:
List of field names (as strings) that are containing the content to analyze.
- query:
The query restricting the set of documents to analyze. In the API, the query should be formatted as a JSON string. By default empty and all the documents in the chosen indices are analyzed.
- analyzers:
List of analyzers to be applied. The available options are:
“tokenizer” - Tokenizes the content with the tokenizer specified with param
tokenizerand stores the result in a new field with name<source_field>_es.tokenized_text.“stemmer” - Stems the content while using the tokenizer specified with param
tokenizerand stores the result in a new field with name<source_field>_es.stems.
- tokenizer:
Tokenizer used for tokenizing the text (used by the stemmer as well!). The available options are:
“standard” (default)
“keyword”
“letter”
“lowercase”
“whitespace”
“uax_url_email”
“classic”
“thai”
Read more about the differences between the aformentioned tokenizers here (all the tokenizers besides
keyword) and here (keywordtokenizer).
- stemmer_lang:
Used by the stemmer to determine the correct analyzer to use. If the input set of documents is not monolingual, it is advisable to left this empty and use automatic language detection instead by enabling parameter
detect_lang.Supported options are:
{ "ca": "catalan", "da": "danish", "nl": "dutch", "en": "english", "fi": "finnish", "fr": "french", "de": "german", "hu": "hungarian", "it": "italian", "lt": "lithuanian", "no": "norwegian", "pt": "portuguese", "ro": "romanian", "ru": "russian", "es": "spanish", "sv": "swedish", "tr": "turkish", "ar": "arabic", (Elasticsearch version >= 7) "et": "estonian" (Elasticsearch version >= 7) }
- detect_lang:
Whether or not to detect the language of each document automatically. If the set of documents is monolingual, it is advisable to define the language via parameter
stemmer_langand turn the automatic language detection off; otherwise it should be enabled.
- strip_html:
Whether or not to strip the documents from HTML.
- bulk_size:
Indicates how many documents are processed per one scroll.
- es_timeout:
After how many minutes of processing one batch of documents (n documents in batch =
bulk_size) Elasticsearch throws a timeout and the processing is suspended.
GUI¶
For creating a new ES Analyzer task, navigate to “Tools” -> “ES Analyzer” and click on the button “CREATE” in the upper left corner of the page. A new window with the title “Apply Elastic Analyzer to Index” opens as a result. Fill all the required fields, select the analyzer (or analyzers) you wish to apply and then click on the button “Create” in the bottom right corner of the window (Fig. 21). The new ES Analyzer task should now appear as a new row in the list of ES Analyzer tasks on the same page (if not, try refreshing the page).
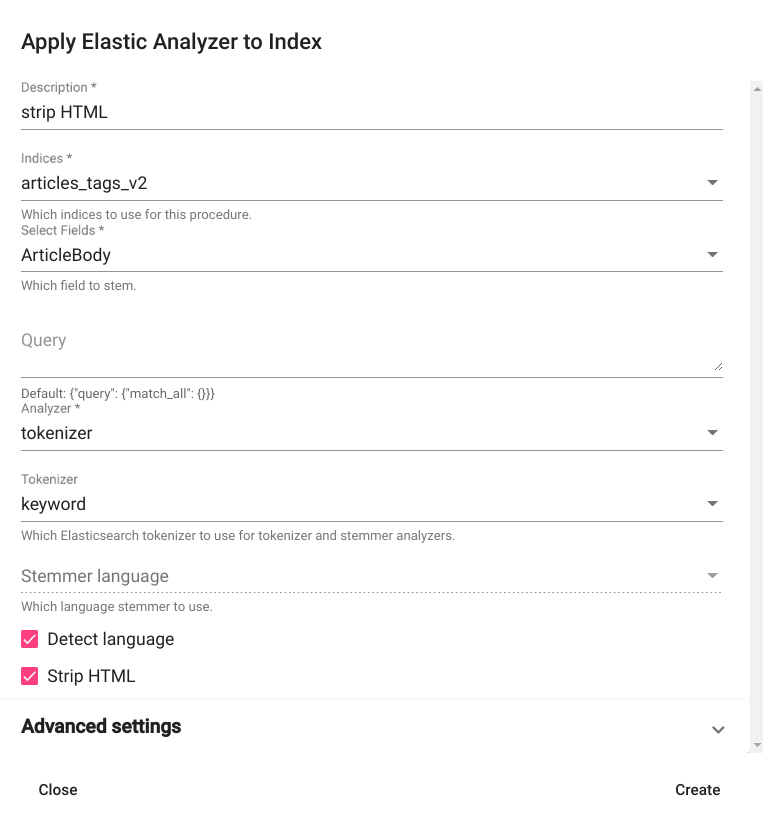
Fig. 21 ES Analyzer creation window¶
After the task has finished (status = “completed”), you can view the results in Search. The output of tokenization is stored in the field <source_field>_es.tokenized_text and the output of stemmer is stored in the field <source_field>_es.stems.
API¶
Endpoint for /api/v1/ : /projects/{project_pk}/apply_analyzers/
Endpoint for /api/v2/ : /projects/{project_pk}/elastic/apply_analyzers/
Example:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8000/api/v2/projects/1/elastic/apply_analyzers/" \
-H "accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Token 8229898dccf960714a9fa22662b214005aa2b049" \
-d '{
"strip_html": true,
"indices": [{"name": "article_tags_v2"}],
"analyzers": ["tokenizer"],
"fields": ["ArticleBody"],
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"detect_lang": true,
"description": "strip html"
}'
Response:
{
"id": 6,
"url": "http://localhost:8000/api/v2/projects/1/elastic/apply_analyzers/6/",
"author_username": "test_user",
"strip_html": true,
"indices": [
{
"id": 3949,
"is_open": true,
"url": "http://localhost:8000/api/v2/elastic/index/3949/",
"name": "article_tags_v2",
"description": "",
"added_by": "test_user",
"test": true,
"source": "",
"client": "",
"domain": "",
"created_at": "2021-07-27T13:56:46.118000+03:00"
}
],
"analyzers": [
"tokenizer"
],
"stemmer_lang": null,
"fields": [
"ArticleBody"
],
"tokenizer": "keyword",
"es_timeout": 25,
"bulk_size": 100,
"detect_lang": true,
"description": "apply tokenizer",
"task": {
"id": 163542,
"status": "completed",
"progress": 100.0,
"step": "",
"errors": "[]",
"time_started": "2021-07-27T16:58:46.886043+03:00",
"last_update": null,
"time_completed": "2021-07-27T16:59:09.632845+03:00",
"total": 0,
"num_processed": 0
},
"query": "{\"query\": {\"match_all\": {}}}"
}
Usage¶
Removing HTML¶
ES Analyzer can be used for removing HTML while otherwise preserving the original format of the text (i.e. without additional tokenization). For doing so, the following parameter combination should be used:
strip_html = true
analyzers = ["tokenizer"]
tokenizer = "keyword"
Example output is displayed on Fig. 22

Fig. 22 ES Analyzer: Removing HTML (result is stored in the field “<source_field>_es.tokenized_text”)¶
Stemming¶
To use the ES Analyzer for stemming documents, the advisable parameter combination is the following:
strip_html = true
analyzers = ["stemmer"]
tokenizer = "standard"
Example output is displayed on Fig. 23

Fig. 23 ES Analyzer: Stemming (result is stored in the field “<source_field>_es.stems”)¶
